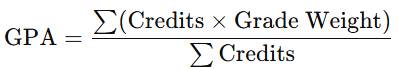Assessment
The assessment system used is relative, a method for evaluating student abilities by comparing them to other students’ skills in the same class. This means that the performance of all students in one class is the basis for assessment. It is assumed that in a class with many students, there will be students with very good, good, sufficient, lacking, and poor abilities.
The students’ abilities are given a value with the letters A, A-, A/B, B+, B, B-, B/C, C+, C, C-, D, E, T, and K, which have the following meanings:
| Assessment Scale | Weight | Alternative Range | Predicate |
| A | 4.00 | 85 – 100 | Excellent |
| A- | 3.75 | 81.3 – 84.99 | Very Good |
| A/B | 3.50 | 77.6 – 81.2 | Good |
| B+ | 3.25 | 73.76 – 77.5 | |
| B | 3.00 | 70 – 73.75 | |
| B- | 2.75 | 67.6 – 69.99 | Satisfactory |
| B/C | 2.50 | 65.1 – 67.5 | |
| C+ | 2.25 | 62.6 – 65 | |
| C | 2.00 | 60 – 62.5 | |
| C- | 1.75 | 53.38 – 59.99 | Below Acceptable |
| C/D | 1.50 | 46.8 – 53.37 | |
| D | 1.00 | 40 – 46.7 | |
| E | 0.00 | <40 | Not Acceptable |
K: empty (no value), incomplete, or non-existent value data because the student has withdrawn from educational activities legally. If the student withdraws illegally, an E value is given.
T: incomplete, incomplete value data because not all assignments have been completed on time with the permission of the relevant lecturer. The assignment must be completed no later than two weeks after the exam scores are announced, and if not met, the T value is changed to E.
Academic Achievement
The evaluation of student performance aims to assess academic achievement throughout the learning process. The assessment is based on the Grade Point Average (GPA) students achieve during their academic activities. In determining the GPA, letter grades must be converted into numerical values according to their respective weightings, allowing the GPA to be calculated using the following formula: